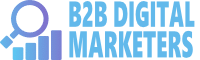In this article, I am going to teach you everything you need to know about semantic SEO and how you can use it for your website to improve your ranking and organic traffic in a step-by-step process.
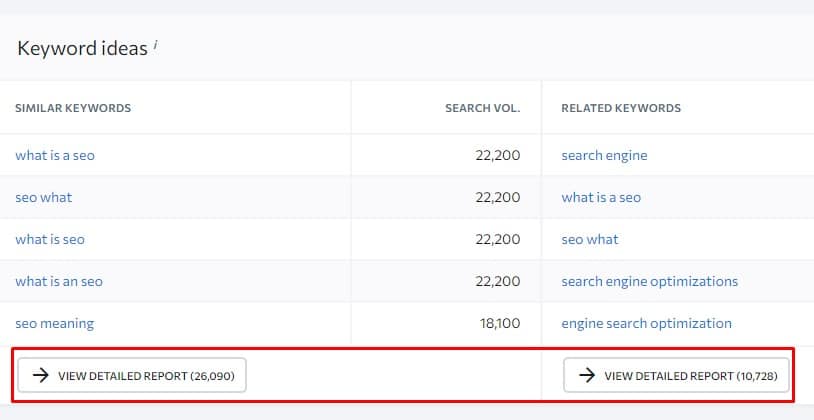
What is Semantic SEO?
Semantic SEO is a process of analyzing key topics and subtopics important to your business to create relevant content by targeting keywords and their relevant words to create topic relevancy and increase topic signals to improve your ranking for an overall niche.
Now, this is the definition of semantic SEO. However, as you can see, semantic SEO means many different things, so let’s explain each of them separately.
First, to understand it, we need to look at Google Semantic Search. Since Hummingbird update in 2013 Google prefers pages and websites that match the search query’s meaning rather than pages with the stuffed matching keywords within the text.
And what it means it prevents stuffing keywords within the content to “win” the favor of search engines in order to improve ranking.

Hummingbird update encourages web developers and writers to use natural language when creating content instead of using forced keywords and stuffing keywords everywhere.

And as the technology is getting better and new updates are rolling out such as RankBrain in 2015, BERT in 2019, Google MUM, and Google Passage in 2021 Google semantic search is getting better and Google can better understand the natural language and the search intent.
Therefore Semantic SEO is about finding the right words or phrases that are commonly used and associated with your targeted keyword.
And this gets us to the second part of Semantic SEO and what it means.
Now, publishing content on your website and including relevant key phrases in your On-page SEO is just one piece of a pie. As I mentioned in the definition, you need to analyze key topics, to create relevant content to increase topic signals.
A well-known SEO strategy from HubSpot the Topic Clusters is specifically targeting this part of Semantic SEO and what it means is that instead of just focusing on targeting SEO keywords, you switch topics in your niche you want to own.
For example, one of the main topics in digital marketing is SEO. So, for me to own this topic I must create as much content around it to create semantic relevance on my website and interconnected together with internal links
And by linking all internal content within that topic to a pillar page, search engines such as Google, Bing, or Yandex can easily scan all the content and understand that there is a semantic relationship between the pages’ content and that my website is about SEO.
Therefore, semantic SEO and SEO overall strategy are about creating relevancy on your website and focusing on topics and not just key phrases.
However, this doesn’t mean that keywords are dead. They are more important than ever before, just you must be more strategic about what keywords you are targeting.
Why Do You Need Semantic SEO?
First and foremost, Semantic SEO addresses some of the most important and latest Google ranking factors and algorithm updates, thus, you can improve your ranking, views, and impressions.
It also helps SEOs and content marketers to create more comprehensive pieces of content with a satisfying amount of information that answers searcher’s questions. Therefore, semantic SEO helps websites being established as the trusted source for the topic within the niche.
And not only it helps with creating content that answers the search question, but also Semantic SEO helps you to create content that matches the search intent or create the exact content your users want and answer their questions.
And because semantic SEO is all about creating as much content around the content with a satisfying amount of information it helps to improve the overall Google E-A-T which stands for Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness.

And overall semantic SEO is the way how you should think about creating content if you want to be successful with SEO and that means:
- Focusing on topics and create as much content around it.
- Provide a satisfying amount of information within your content.
- Optimize your website and content for your niche.
Thus, since Google implemented algorithms that support semantic SEO, we can see fewer and fewer spammy websites that are run by one person who writes about everything, and we can see more niche websites dominating the search in an area of their expertise.
And now, let’s move on to how you can optimize your website and page for semantic SEO in a step-by-step process.
Step #1: Find Your Main Topics
The first step in Semantic SEO is to find the main topics you want to own in the search.
This highly depends on the industry you are in and on what you are focusing on there. It is crucial to decide the right topic to not only generate organic traffic but also leads from organic traffic. Because remember organic traffic doesn’t pay the bills.
Now, most likely you can come up with main topics quite easily as often your industry, products, or services are considered the main topics.
For example, in the digital marketing niche, the main topics you can target are “SEO”, “lead generation”, “content marketing”, “email marketing”, “digital marketing”, “technical marketing”, etc.
Another example could be a computer eCommerce shop where the main topics could be “keyboard”, “computer mouse”, “gaming computer”, “gaming laptop”, “computer screens”, “graphic cards”, etc.
As you can see, anything general that can have more subtopics could be potentially your main topic. The main topic is also called the seed keyword and it is used to find relevant subtopics.
Also, before we get started with searching for keywords to be qualified as the main topic the keyword must:
- Has high search volume. This depends on the industry you are in. In some industries, it could be tens of thousands and in others, it could be hundreds of thousands.
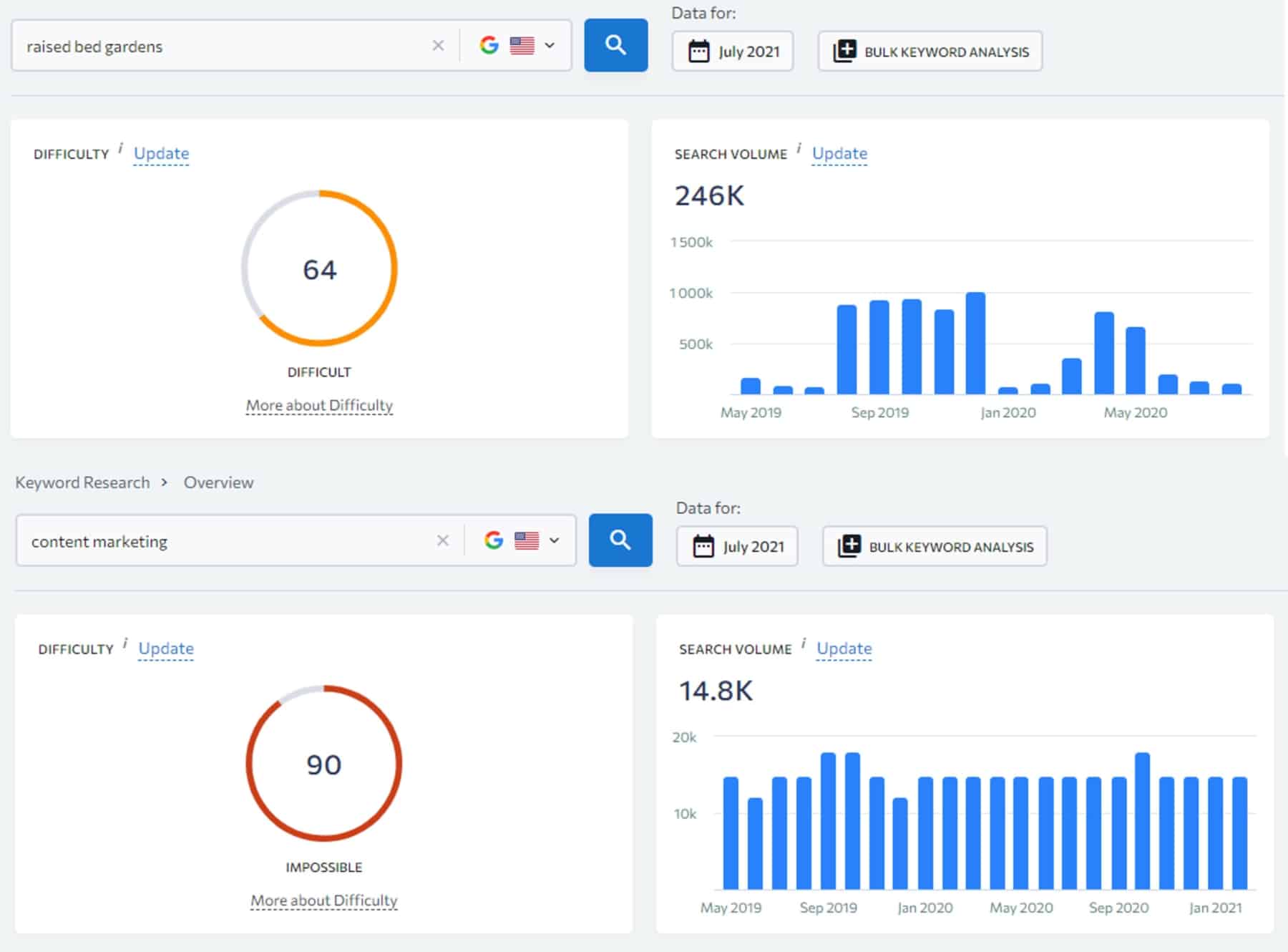
- Has a lot of keyword ideas. Usually, if the main or seed keyword has at least 2,000 keyword ideas, then you will be able to create at least 20 subtopics to target. More in step #2.
- Cannot be too generic: Often one-word keywords like “car”, “marketing”, “computer”, “technology” and others are too broad to be targeted. Therefore narrow down your target keywords to a more specific type of category.
To learn more about seed keywords and keyword research you can watch my video here:
So, do not go for the extra-large keywords with hundreds of thousand keyword ideas because if the keyword is too broad it would be extremely hard to create enough content to create topic relevancy because it can mean anything.
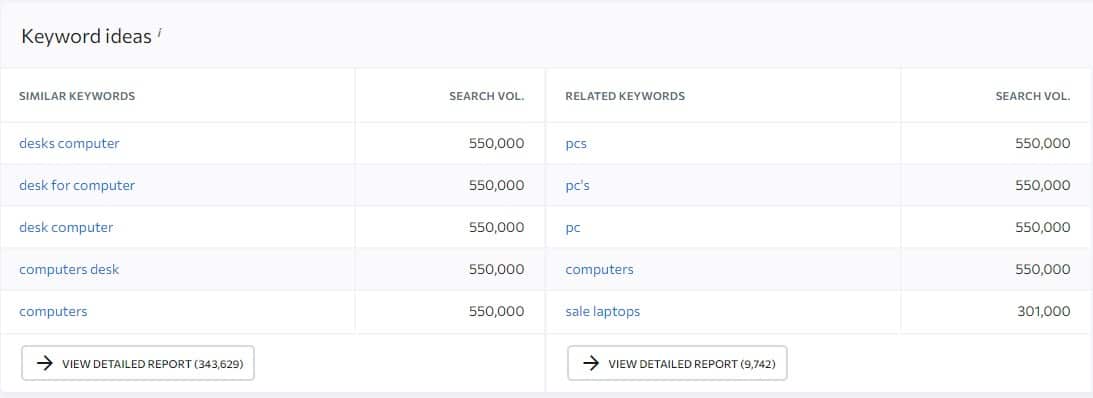
First, I recommend you stay with topics with a maximum of 50,000 keyword ideas if you are using SE Ranking unless you have a large content marketing team.
With that let me show you my 3 favorite ways to find main topics or seed keywords within your and other niches.
And for that let’s suppose I am in the gardening niche, and I want to find seed keywords to set an example. Also check out my guide for SEO tips for Landscaping.
Technique #1: Competitor Analysis
So, the first technique to find topics to write about to improve my semantic SEO is to analyze my competitors.
Now because I don’t know any website about gardening, I can just simply put the keyword “gardening” into Google search, and I can choose from any of the top-ranking competitors.
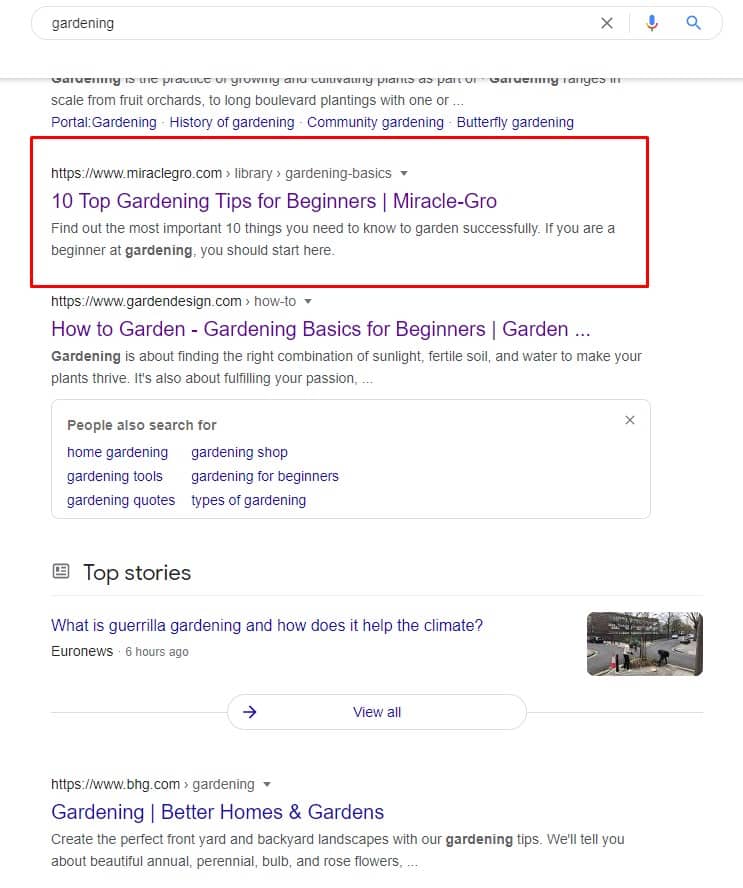
And I have chosen Miracle Gro because if I would create a gardening website, then it would be structured like this, Therefore I found this website as a great competitor and starting point to find main topics.
Anyway, now when I have the competitor website, I can plug it into SE Ranking competitive research tool, select my target location and hit analyze. Of course, you can also use different SEO tools to do that.

And here, I will get important information about my competitor’s website such as their organic traffic, paid traffic, domain trust, and their organic keywords report.
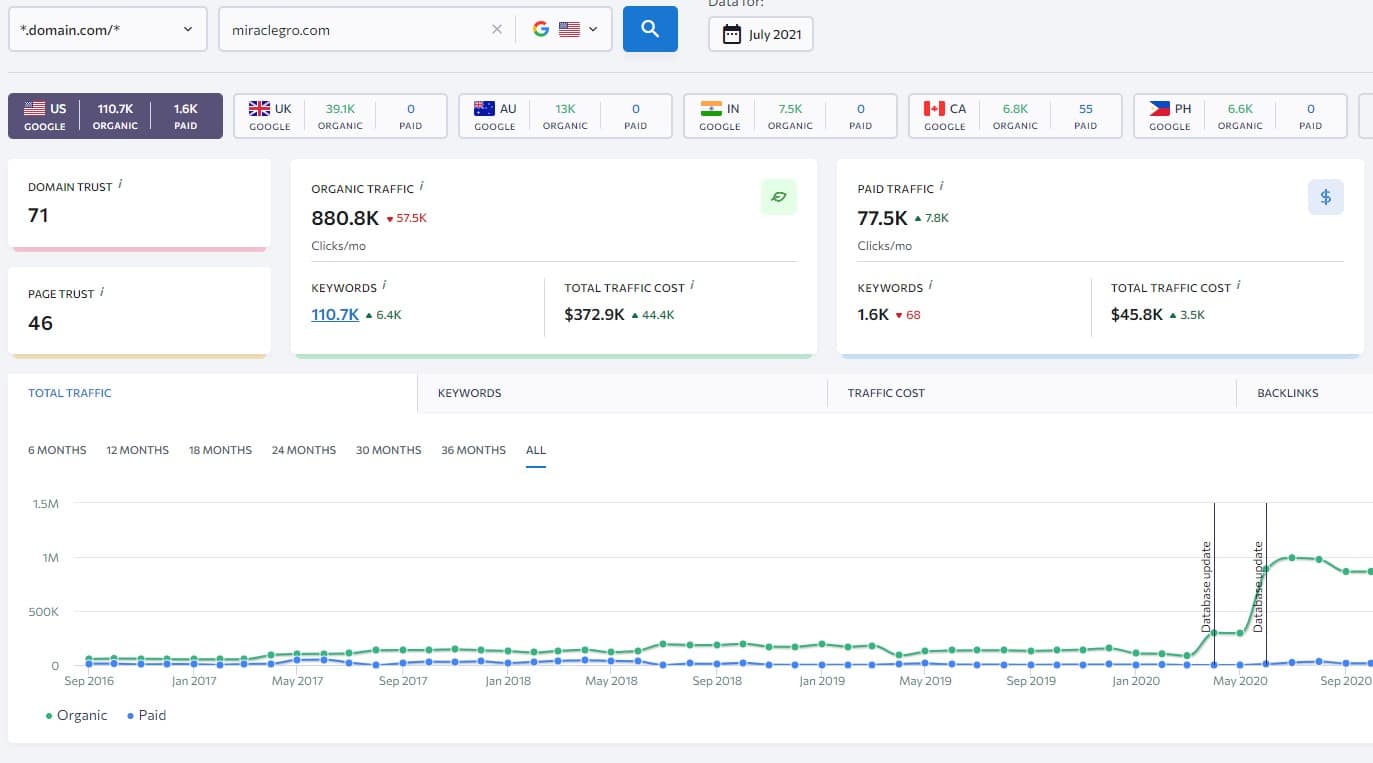
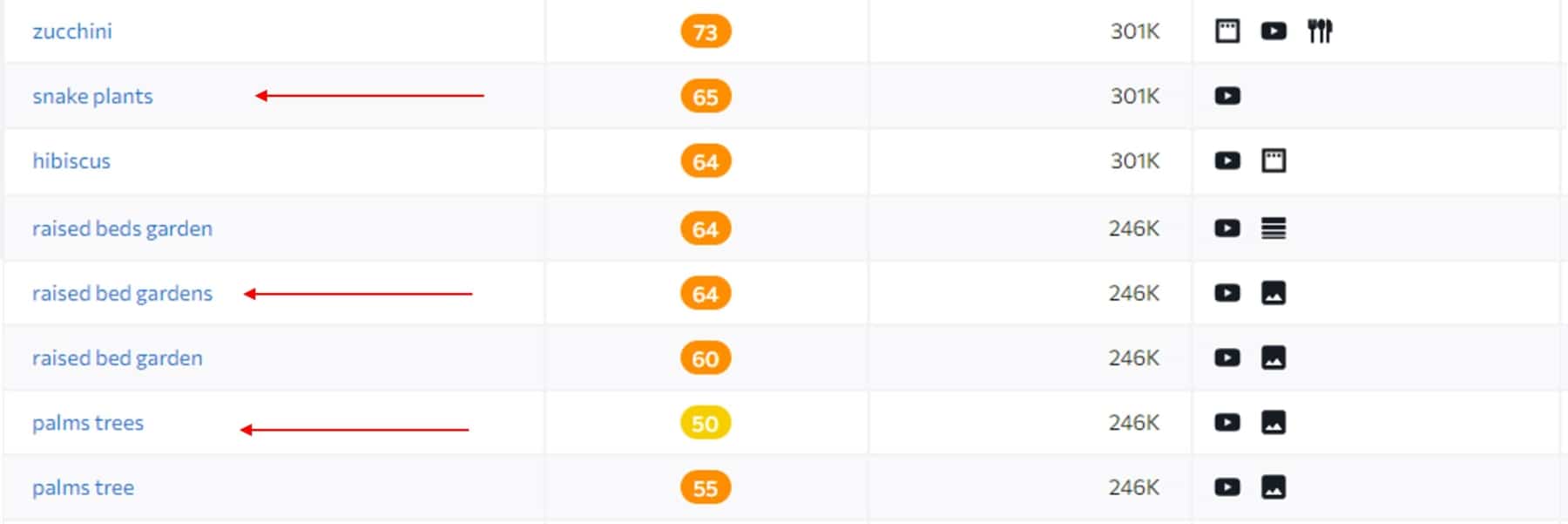
And by clicking on the number of keywords I will get their list of keywords they are ranking for along with other helpful information such the keyword difficulty, search volume, website ranking position, and the traffic the keyword brings to the website.
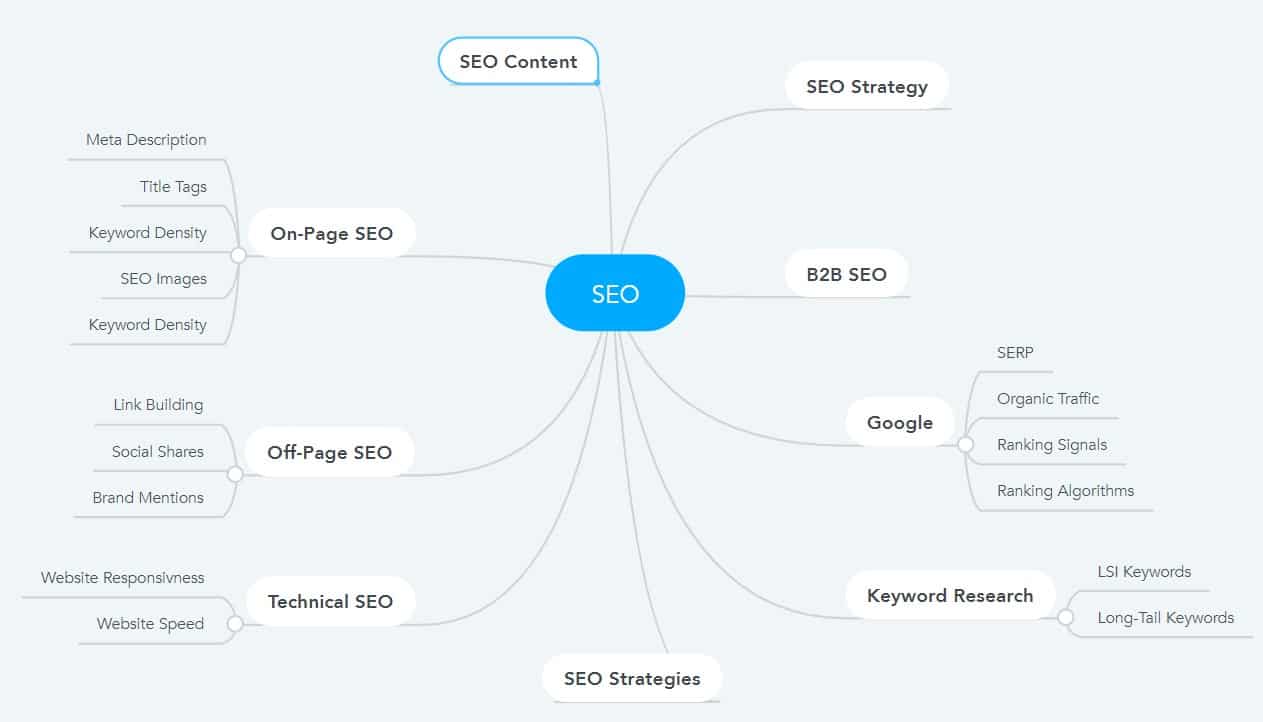
And by scanning their keywords I can find some interesting topics that I can start targeting on my website. For example, topics like snake plants, palm trees, or raised bed gardens are some excellent main topics.
Technique #2: Wikipedia Page
Another great place to find main topic ideas is using Wikipedia.
For example, the Wikipedia page on Gardening is full of great ideas for main topics such as container gardens, root vegetables, leaf vegetables, or ornamental plants.

Again, you don’t need to and shouldn’t target everything. I recommend you target topics that are closely related to your products or services.
For example, if I am selling vegetables, then I would pick the topics “root vegetables” and “leaf vegetables” as these are super relevant to my business and I can naturally include my products within the content later.
Technique #3: Brainstorming
And the last technique is brainstorming.
Probably the most effective technique to come up with main topics closely related to your business is to talk to your sales, directors, customer service, or any subject matter experts within the company and they will probably give you tons of great and super relevant topics ideas you should create content about.
So, these are some of the strategies you can use to generate main topic ideas. And once you have your topic, we can move to the second step.
Step #2: Generate Your Subtopics
The second step is to generate your subtopics for your main topic or a seed keyword.
A great way from HubSpot to determine if the keyword can be considered the main topic or in their case pillar page is:
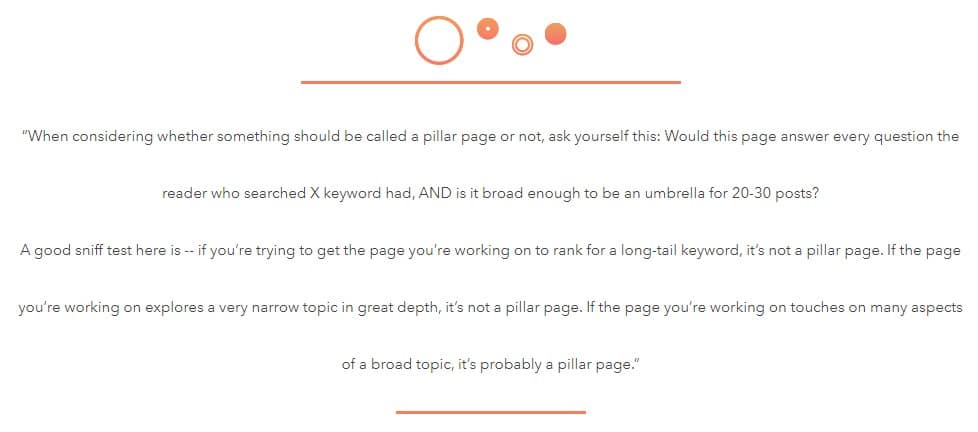
With that let me show you an example of how you can find subtopic ideas for the main topic “raised bed gardens” that I have found in step #1.
First, I fire up my keyword research tool from SE Ranking, enter my targeted keyword, select my location, and hit analyze.
Now, SE Ranking separates keyword ideas into three different keyword ideas categories, I found it super helpful for any keyword research strategy as it helps to concentrate on the specific keywords you need, but when I am searching for subtopics, I am going through both “Similar Keywords” and “Related Keywords” ideas.
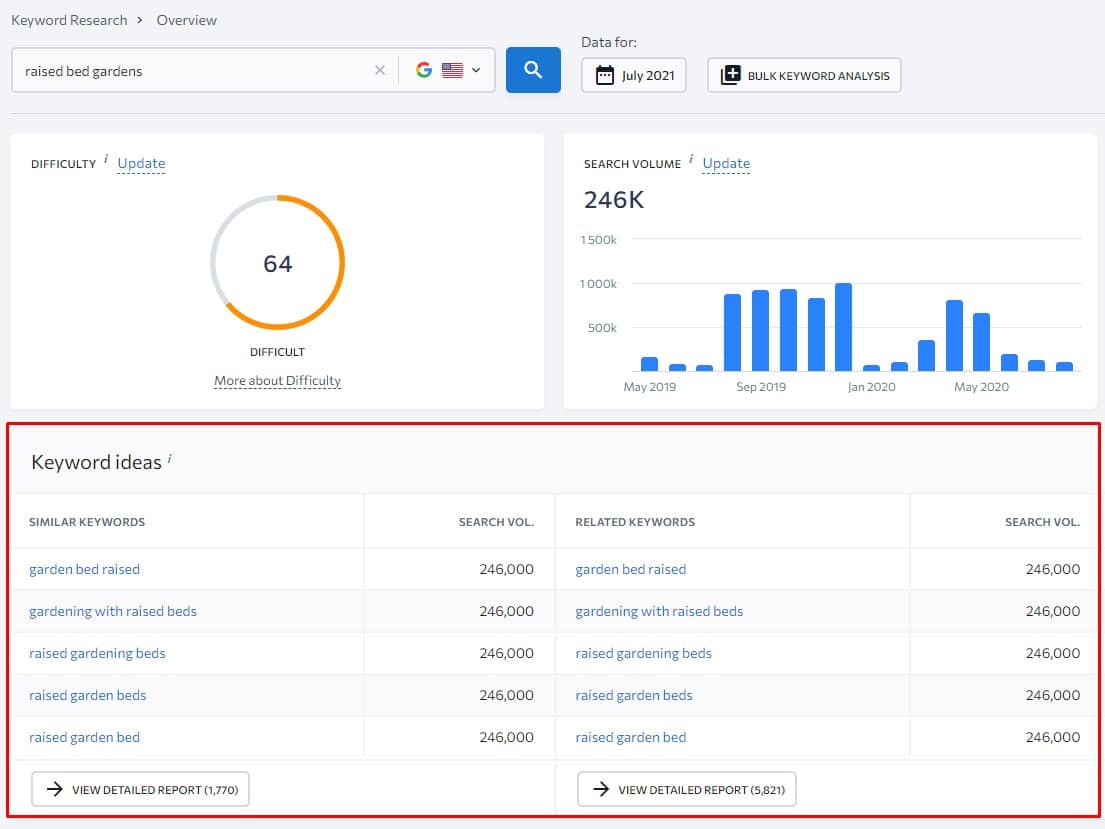
So, let’s started with the “Similar Keyword” report and scan for the keywords there. Once I am done, I can move to the related keywords report by switching the taps.
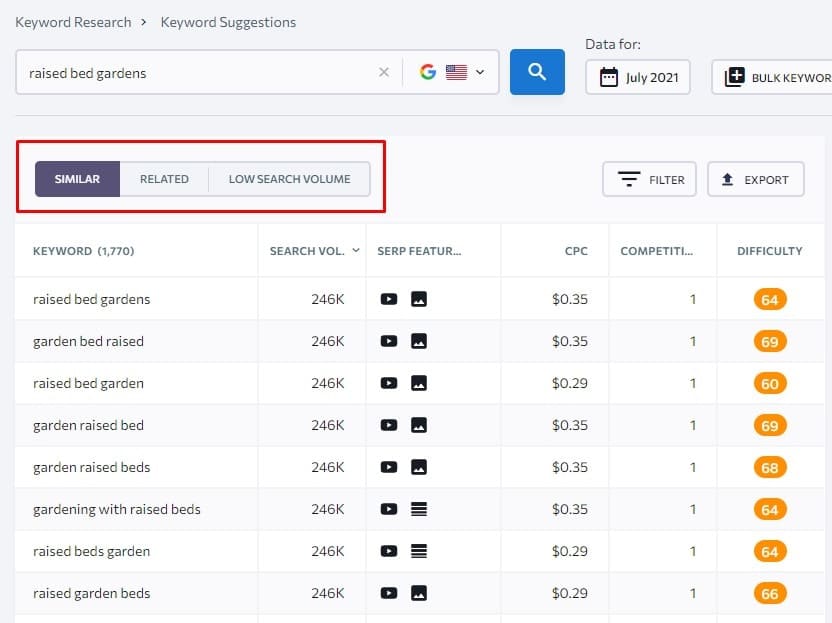
So, here I scan the keywords and any keywords that make sense to me could be subtopics I will include in my topic cluster. (Note: Please be aware I have no idea and knowledge in gardening beds whatsoever)
For example, the keywords “raised bed garden plans”, “raised bed gardening kit, “raised garden bed diy”, “raised garden beds ideas” and “how to build raised garden beds” are for me great keyword ideas for subtopics as I can create an entire blog post to target this keyword.
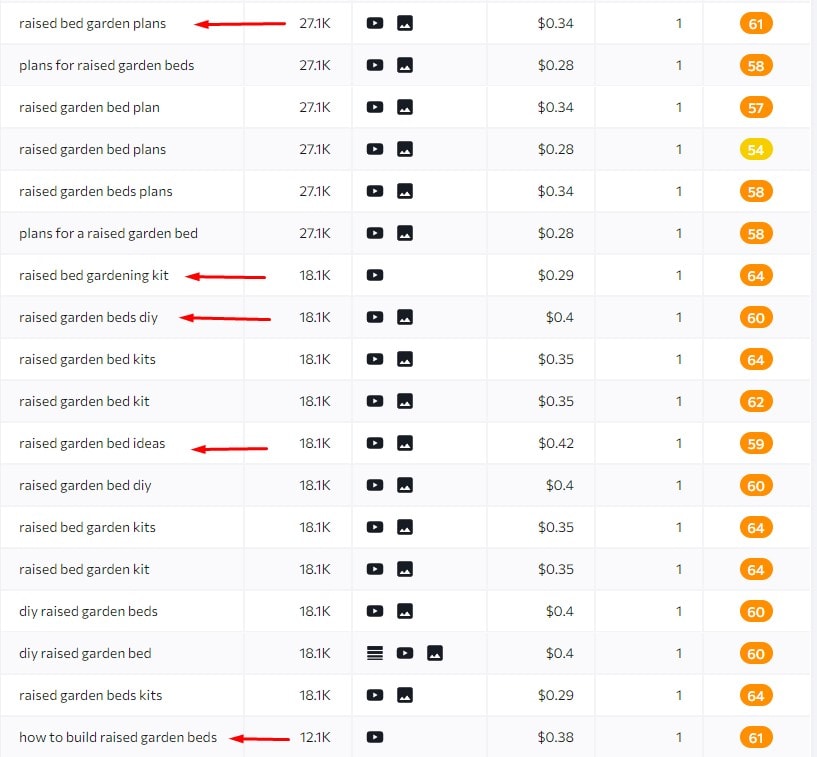
Pro Tip: If you are not sure if the keyword can be subtopic or not, just pop it into Google and if the keyword is being targeted by another website with a specific blog post or page then it is a subtopic keyword.
So, I can start creating my topic cluster and adding more subtopics. Now depending on the tool, you are using you enter your keyword. A simple spreadsheet will do or if you like more visuals like me, you can use the MindMeister mind mapping tool.

Remember you want to find as many subtopics as you can for the main keyword to create topic relevancy for your semantic SEO so Google and users can acknowledge your website as the go-to place for the subject.
Step #3 Find Search Intent
The third step once you have your subtopics is to start creating content to target the subtopics/keywords and for that, you need to find search intent for your targeted keyword.
Search intent means the reason behind the search query or what the users want when they type the keyword into the search box.
This is important to know when you want to create content on your website to target the keyword, so you create the type of content users are searching for.
For example, let’s say I want to target the subtopic or keyword “raised garden bed ideas”. So, to find the search intent I can just pop the keyword in the free tool SE Ranking Google Location Changer to get precise results for my targeted location.
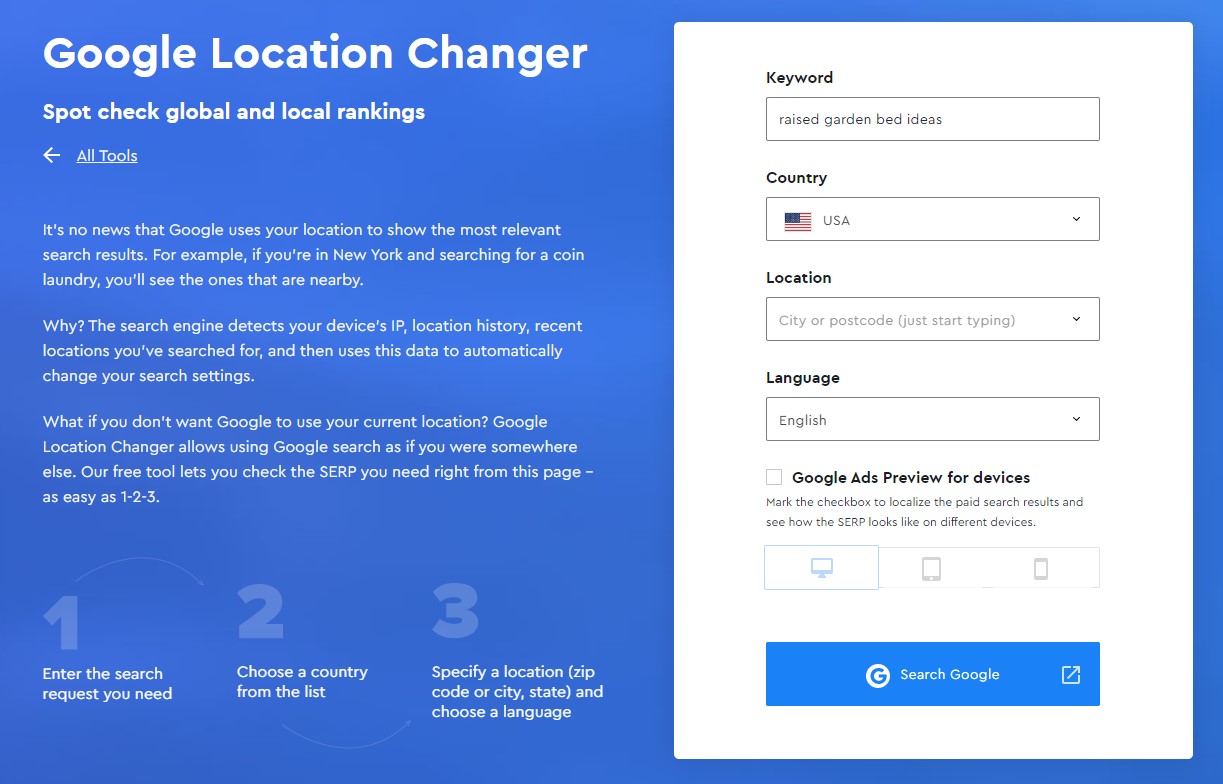
And now based on the search results I will create the type of content users want. So, for my targeted keyword I can see that most of the top-ranking pages are listicle blog posts. Therefore, I can create my own and unique listicle blog post to the targeted keyword.
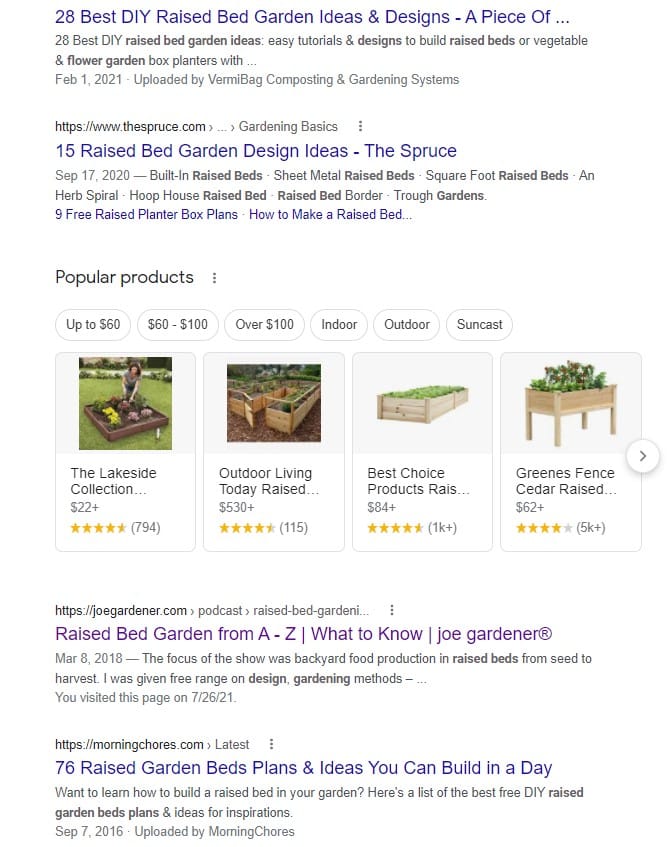
Another example could be the keyword “raised garden bed metal” where based on the search results I would have to create a category product page. However, let’s say I don’t have my product and do not have an eCommerce shop on my website.
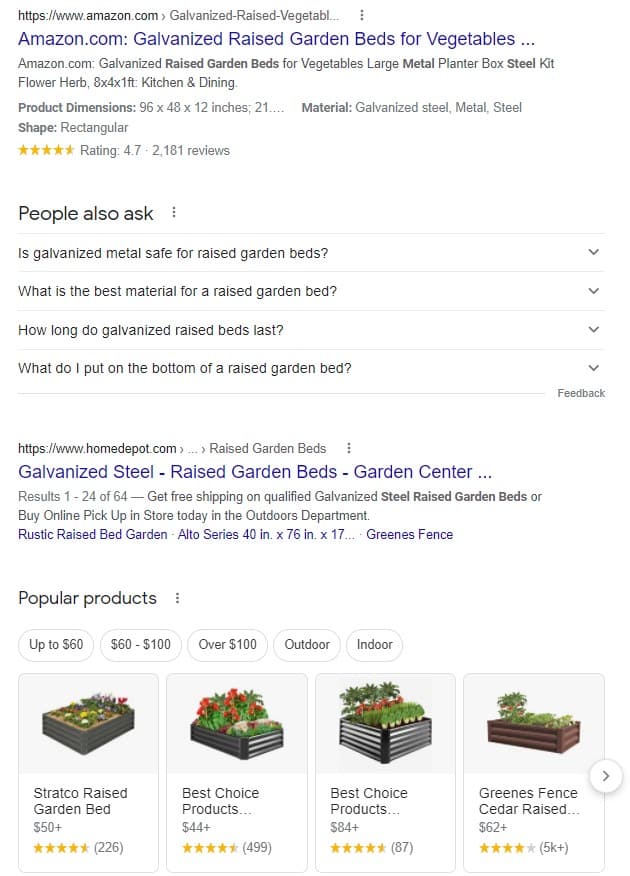
Therefore, I cannot target this keyword because I cannot match the search intent. However instead of just targeting the keyword “raised garden bed metal” I can add a keyword modifier “best” and target the keyword “best raised garden bed metal”.
And now based on the search results I can create a listicle blog post with the best-raised garden bed metal and add my affiliate links to make a few bucks if somebody buys the product via my link.
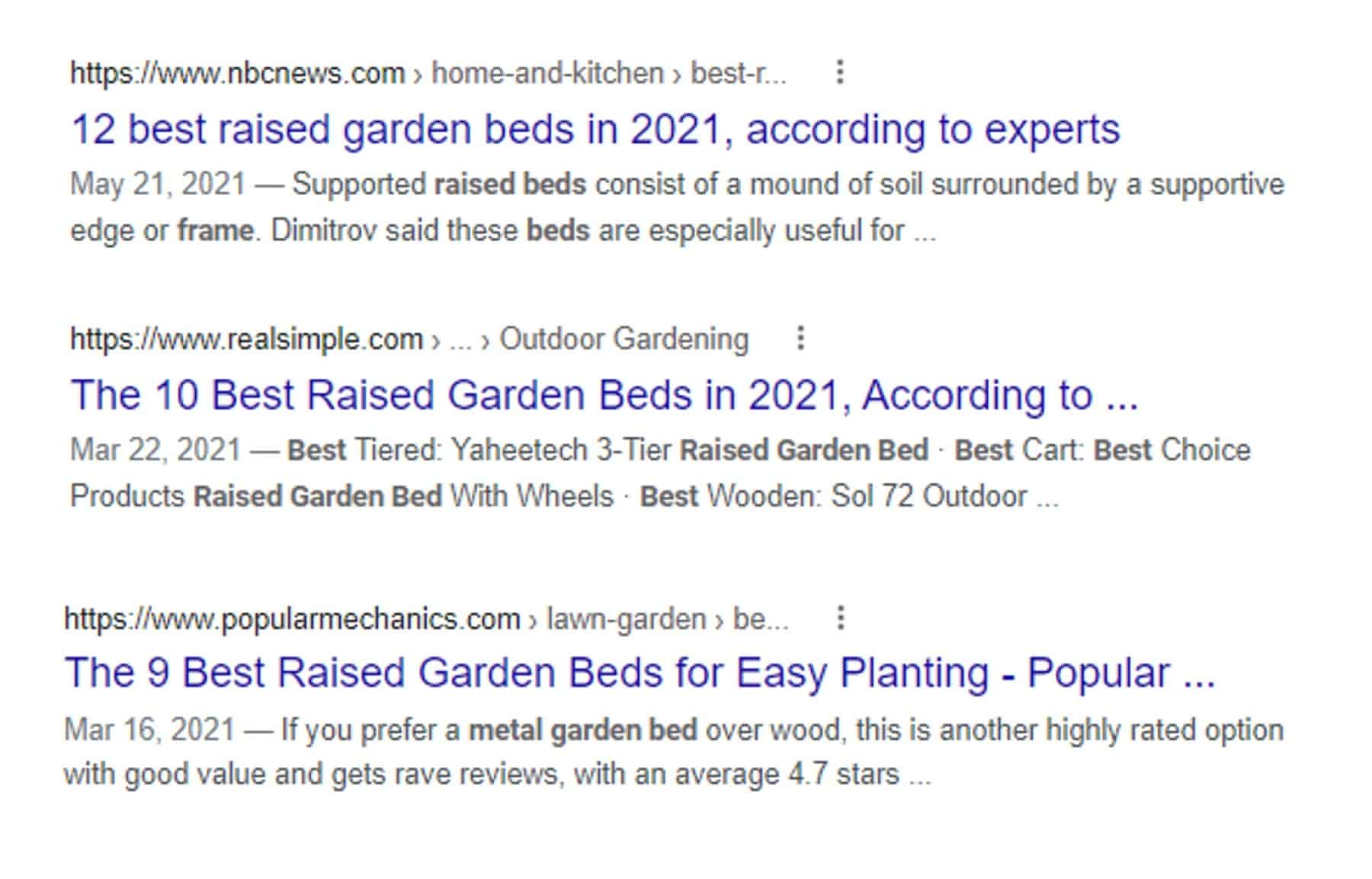
Therefore, it is important to analyze a search intent for semantic SEO to match the searcher’s needs when they are entering the keyword to maximize the organic traffic potential.
Step #4: Find LSI Keywords
The fourth step is to find LSI keywords for your targeted keyword.
Once you understand the search intent of your targeted keyword, you can start searching for LSI keywords.
LSI keywords are related keywords to your targeted keyword and search engines like Google associate those together to better understand your content.
And using LSI keywords will help you with creating your content outline as you will collect important talking points that you should include within your blog posts.
And to learn everything about LSI keywords you can watch my video here:
However, let me share with you two techniques for how you can find LSI keywords for your targeted keyword. And for this let’s stick with the same keyword “soil for a raised bed” and create an outline.
Technique #1: Using Keyword Research Tool
The first technique to find LSI keywords is using a keyword research tool.
Simply enter the keyword “soil for a raised bed”, enter my targeted location, and hit analyze.
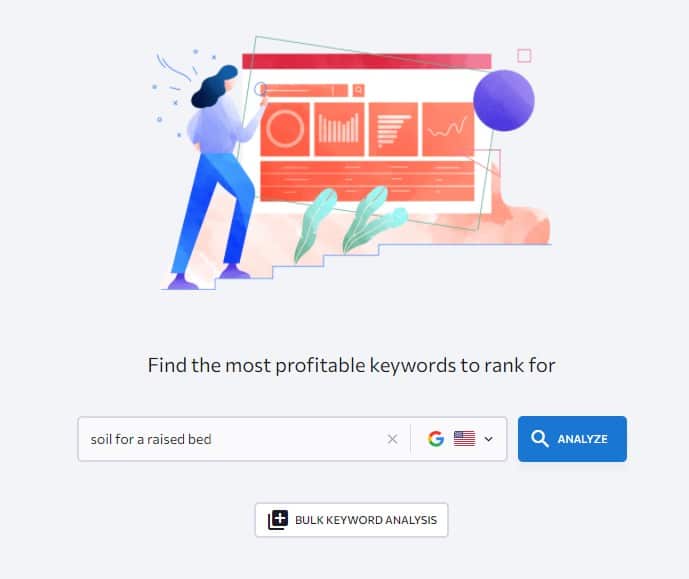
And then open the “Similar Keywords” report.
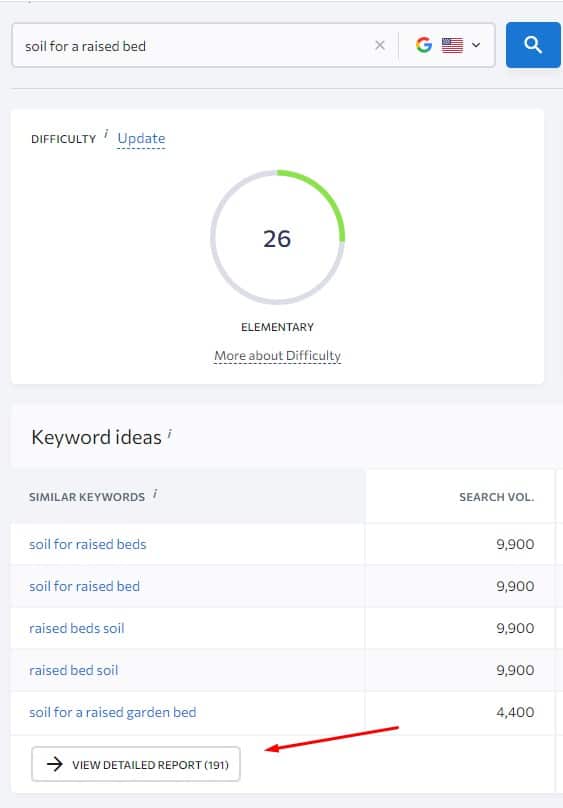
And here I will be scanning the list of keywords to find any related keywords that I can include in my article as a heading, FAQ, or just mention it within my text.
And for example, the keywords “best soil for raised garden bed”, “raised bed garden soil mix”, “best soil for vegetable garden in raised bed”, “how much soil do i need for a raised bed”, and “best soil for tomatoes in raised beds” are great examples of LSI keywords I can include within my article to improve my semantic meaning, add comprehensiveness and more value to my article.
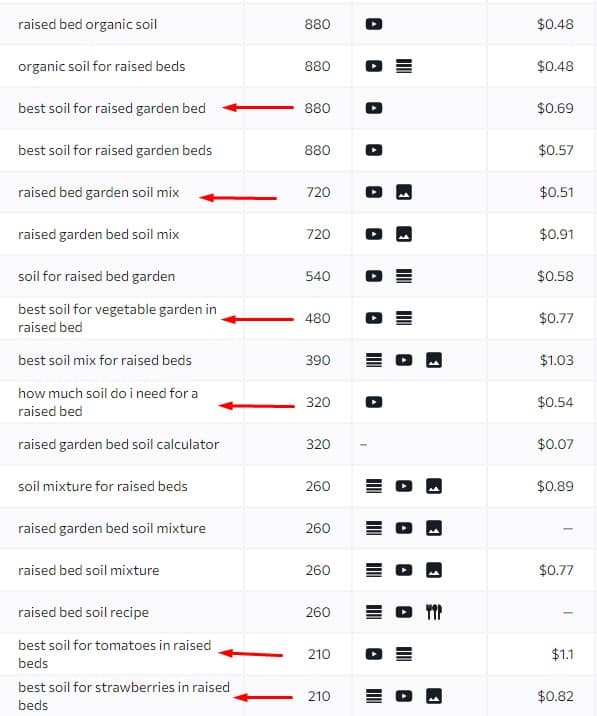
So, let’s pop those keywords and a few more into my document as talking points.
Technique #2: Analyzing Competitor Ranking Pages
The second technique to find LSI keywords is to analyze your competitor’s top-ranking pages for the targeted keyword and see what keyword variants their pages are ranking for.
To do that I will analyze my targeted keyword in SE Ranking Keyword Research tool and then open the competitor keyword report for the top-ranking pages to see the ranking keywords their pages are ranking for.
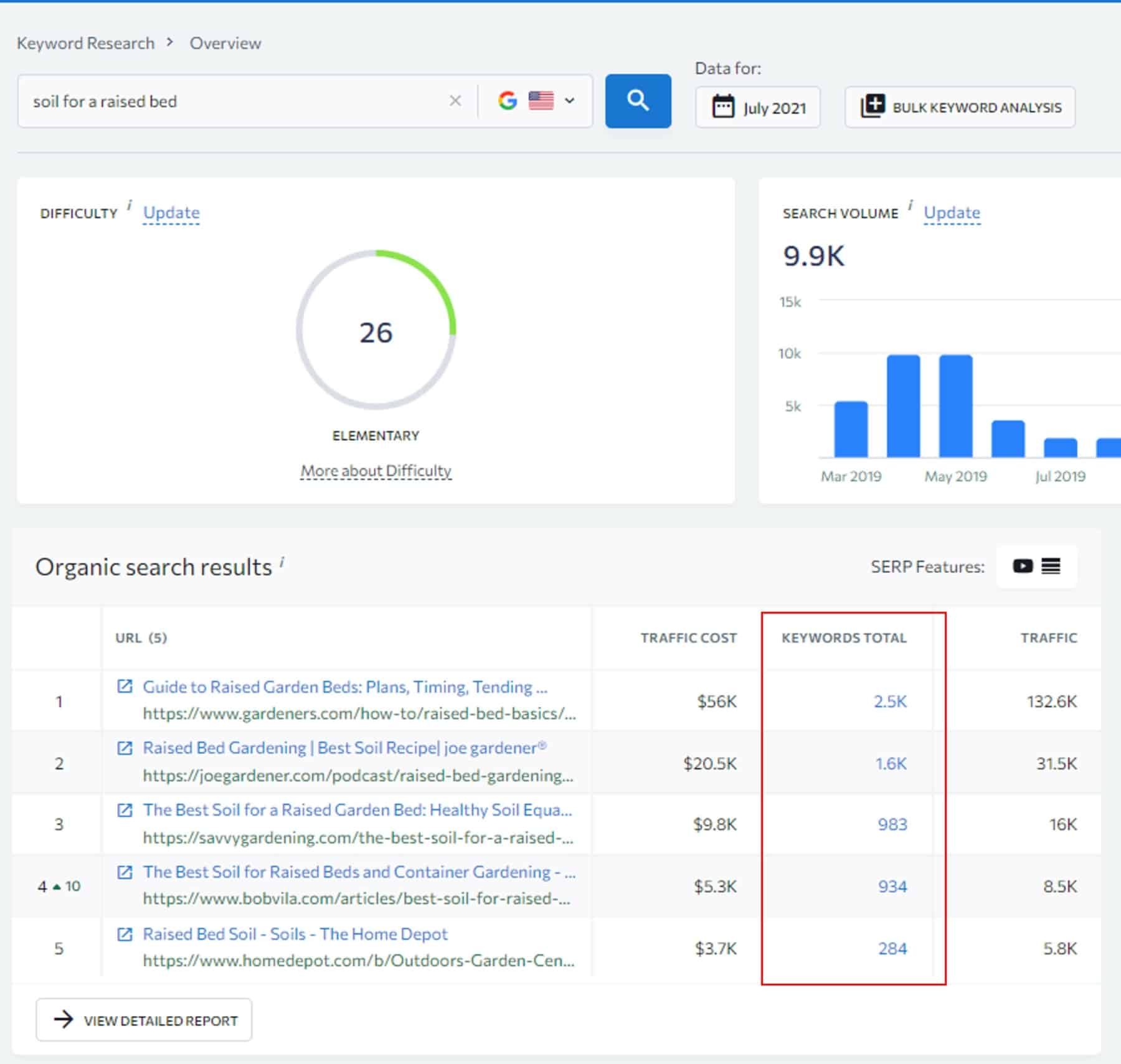
And here I have a list of proven keywords that Google associates with my targeted keyword and users are using to find related information to the keyword.
Therefore, analyzing this list and including any relevant keywords within my web page can improve my web page’s topical relevancy, ranking, and organic traffic, and possibly I can outrank my competitors.
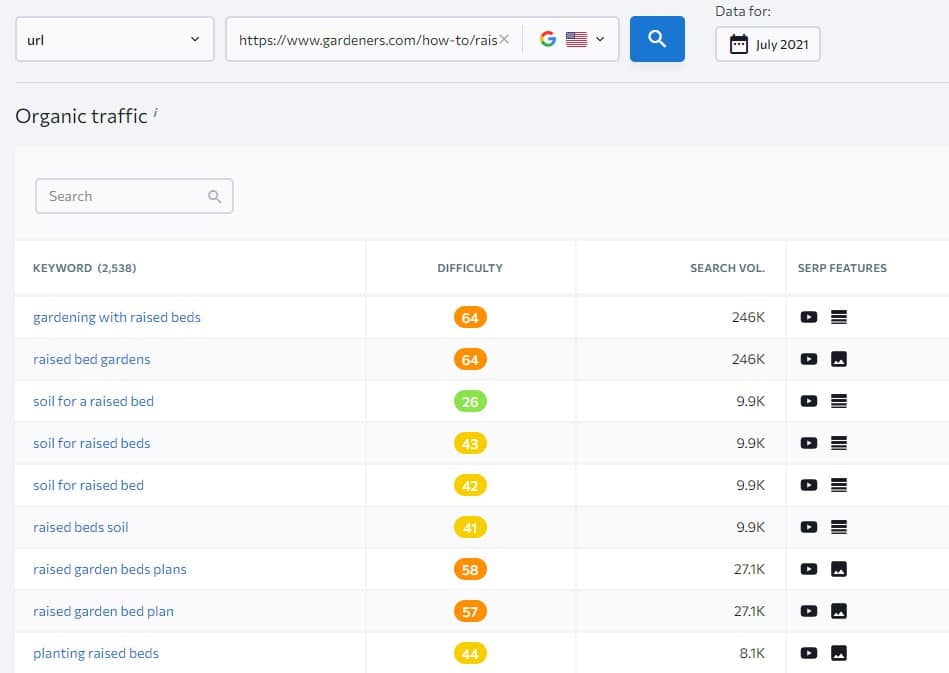
So, I have scanned the list of ranking keywords and found a few that I believe should be mentioned or addresses within my content and add them to my article document.

That is why LSI keywords are important for your Semantic SEO because as you can see you can add more value to your content and directly answer the questions and provide the information your users are looking for.
Technique #3: Google
And the last technique I want to be mentioned where you can search for it on Google.
Simply pop your targeted keyword into Google Search and scroll all the way down. Here you will get other interesting ideas that you can include within your outline.
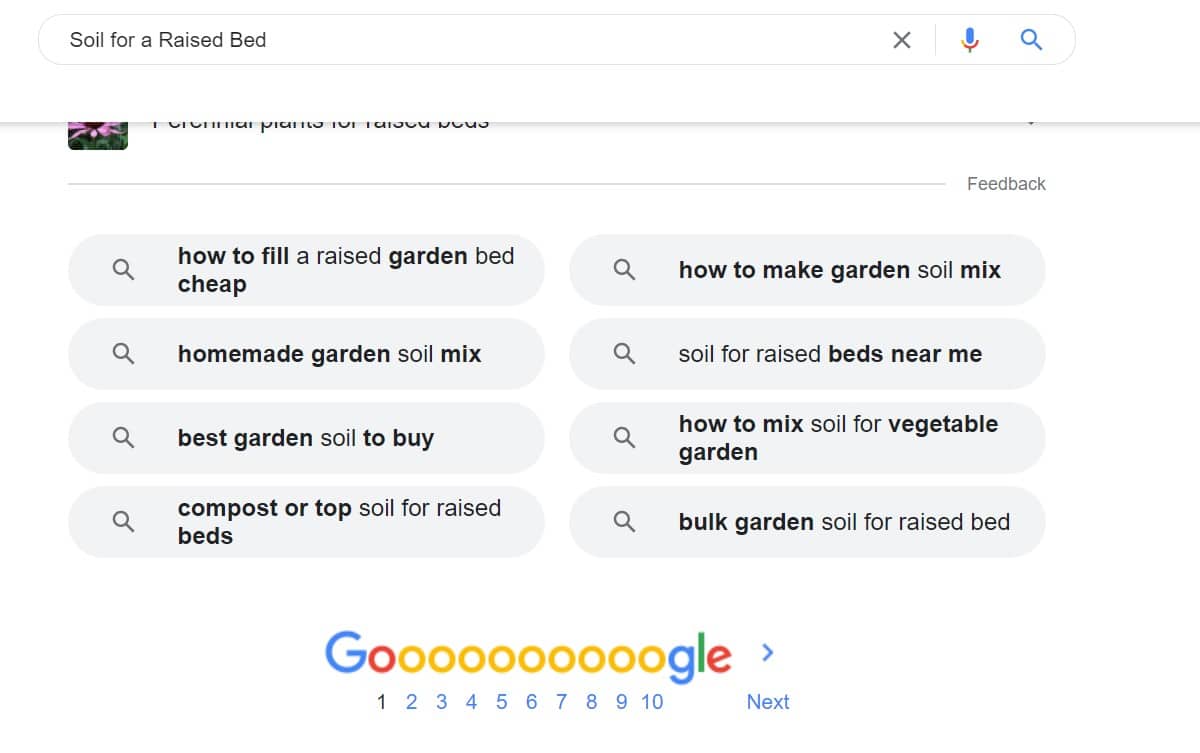
So, let’s pop some of these bad boys into your outline and let’s keep searching.
And once you have the LSI keywords that you want to use in your article it’s time to move to the next step.
Step #5: Collect Relevant Questions
And the last step of your Semantic SEO is to collect relevant questions to your targeted keyword and answer them in your blog post.
Answering questions related to your keyword can help you earn featured snipped by answering directly related questions.
Answering questions can also help you appear in the “People Also Ask” box which means you can rank for more competitive keywords and increase your organic traffic.
This is a very important part when you are preparing your article outline and collecting LSI keywords to not forget about including questions and answers within your blog post.
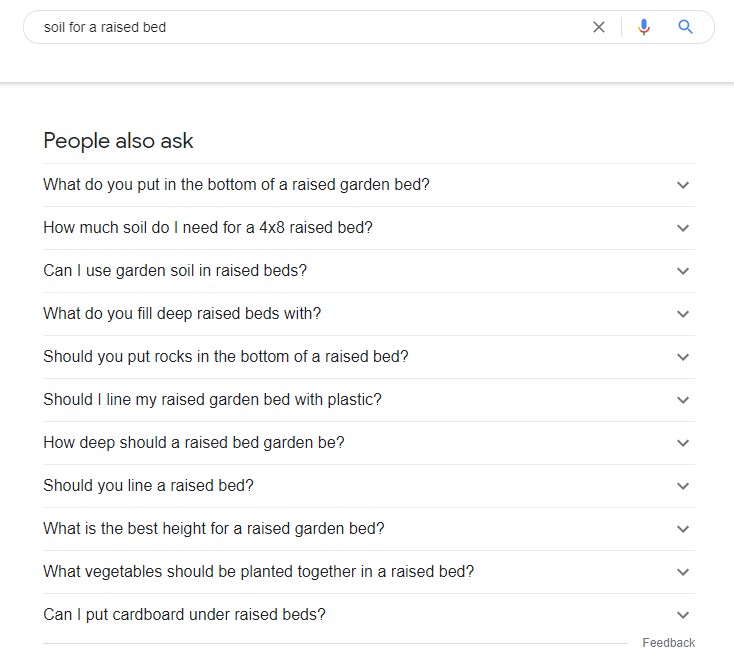
With that let me give you an example of our targeted keyword “soil for a raised bed” how you can find related questions.
First and most importantly I will check the box “People also ask” in Google search if it appears for the targeted keyword. If it does, then I will collect any relevant questions that I can answer within my blog posts and included them within my article outline.
Another place where I can search for relevant questions to answer is using the website Answer the Public. Here I can enter my targeted keyword and get interesting questions. This is definitely a great place to improve your content Semantic SEO.
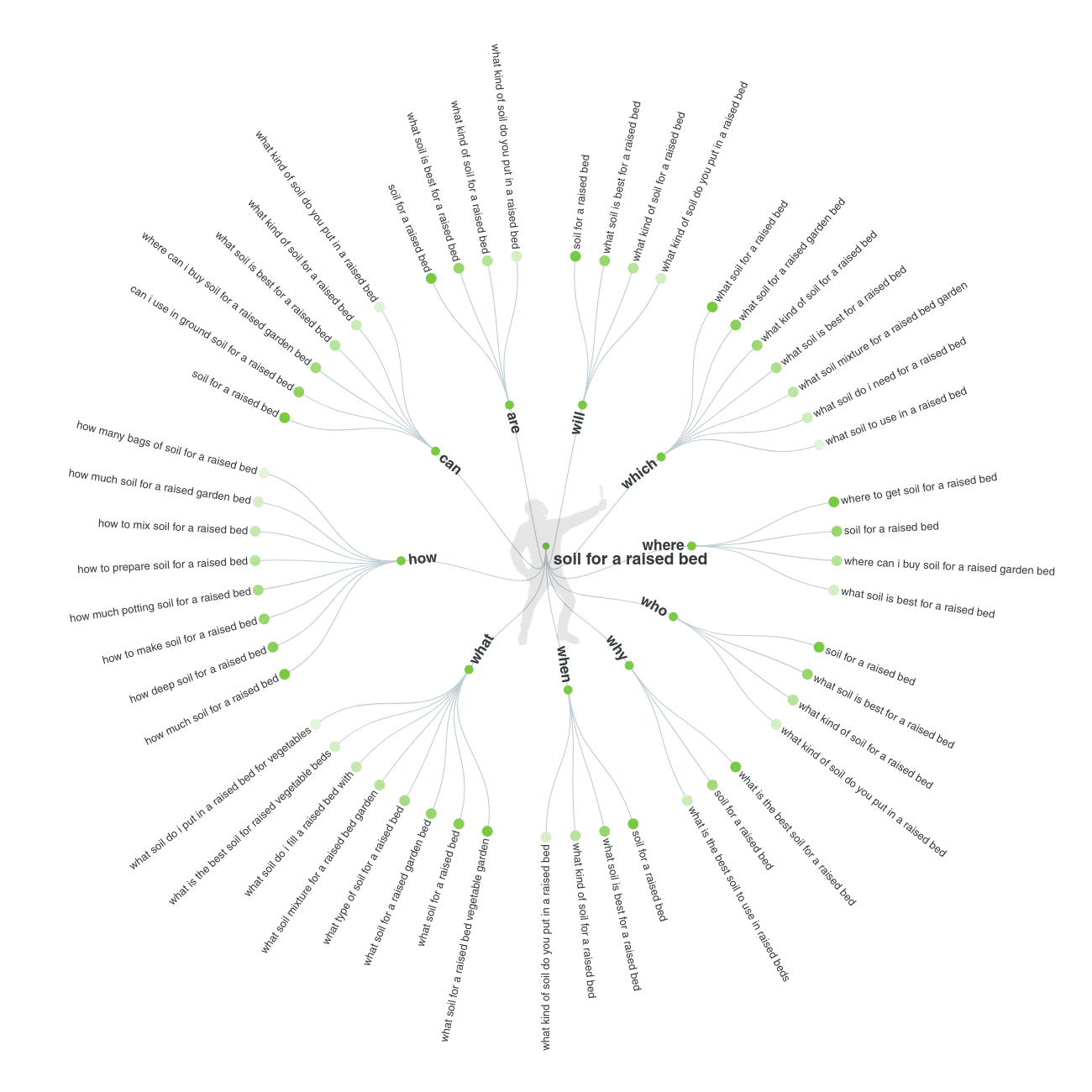
And lastly where you can search for relevant questions is from forum websites like Quora or Reddit. For me forum places are often must-go places to get some interesting ideas as often, if people cannot find an answer on Google they come to forums. Therefore, this is a good indication there is demand but not supply.
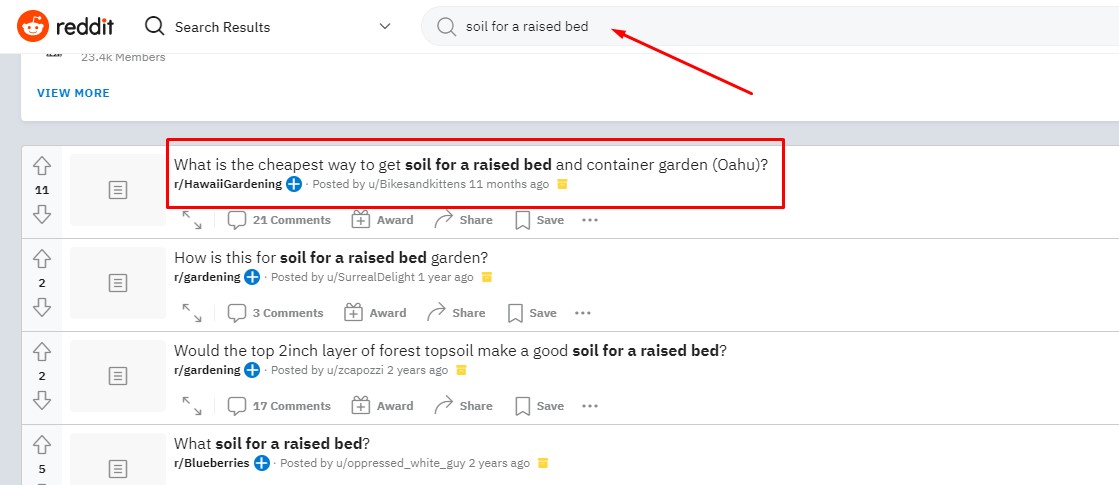
So, once you collect all your questions you will have a solid outline and foundation for your content to create a comprehensive and awesome piece of content that brings tons of value to your users.
As you can see we have created an awesome outline for the keyword “soil for a raised bed” and we are ready to start writing our content and optimize it with different types of SEO strategies.
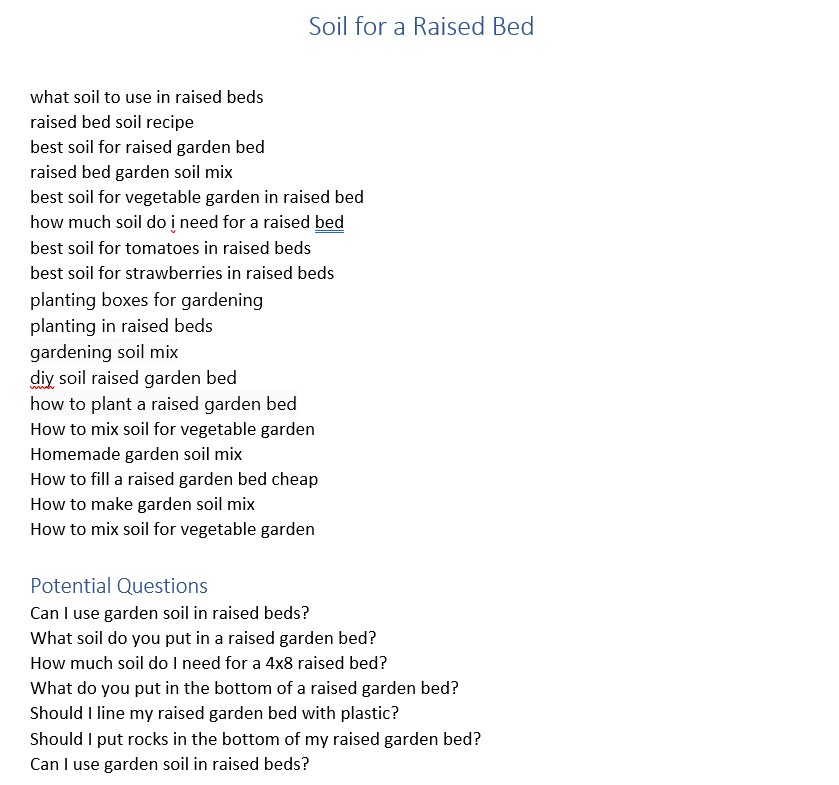
However, remember that you don’t need to include every singly relevant keyword and question you have found. Now, these are only suggestions to create your outline and you should use your knowledge and expertise to create a logical structure of your outline.
Don’t try to overdo it and sometimes less is more. Also, you don’t need to precisely follow the keywords or questions, but you can rewrite it to fit into your context and sentence. Google is smart enough to recognize the answer to a question even when rewritten.
Final Advice
Writing content for Semantic SEO doesn’t need to be hard. Remember that Google is trying to promote natural language with plenty of value.
However, all these steps help you to include additional important points to your content to improve the semantic meaning and ranking of your page.
But you should take everything with pinch of salt and not stuff every single keyword and question you find during the process.
Remember the key is to have content that naturally flows and provides value to users without confusing your readers.
Because at one point you will be able to find plenty of ideas and then it is about prioritizing what’s important and you should include and what can be avoided to not confuse your readers.
This thin balance between too much and too little information within your content is often what you will be struggling with once you get hang of it.
Related Articles:
- 101+ B2B SEO Statistics You Should Know in 2025
- Blog SEO: Best Tips & Practices to Get You Started
- 12 Best Surfer SEO Alternatives & Competitors (Free & Paid)
- B2B SEO vs B2B SEM: What’re the Differences and Which Strategy is Better?
- Off-Page SEO: Learn Everything You Need to Get Started
- On-Page SEO vs Off-Page SEO [infographic]
- How To Do Keyword Analysis for Website in SEO
- SEO Keyword Mapping: The Trick to Perfect SEO
Also, check out our SEO hub page to find all our SEO resources.
Disclaimer
Some pictures are coming from Freepik and some of my links are affiliate links, which means if you purchase something, I might get some small commission as a reward for reference. Of course, I am actively using all these services and products, and I only affiliate products or services I have full trust in their quality!
Support the B2BDigitalMarketers
Hey, Eduard here.
As a solo blogger with limited resources, I need your support to keep creating in-depth SEO content like this. Please consider joining my Patreon community to help this site grow.
Your pledge – no matter how small – will enable me to dedicate more time to sharing actionable tips and strategies. With your help, I can take this project to the next level and really make a difference for other SEOs and marketers.
I would sincerely appreciate you joining me on this journey as a founding patron. Together, we can build an amazing resource hub. Hope to see you on the inside – thanks for your trust and support!